Hari Swaminathan – Options Foundation – Time Decay, Implied Volatility, GreeksBasic knowledge of Call Options and Put OptionsIf you’ve not taken the Options Call and Put Options race, you can find it.DescriptionSECTION I – TIME DECAYTime decay is a pivotal component of Options Strategies. In fact, time decay alone is responsible for the majority of advanced option strategies. In this part of the race, we are going to study the concept in detail. Options are “wasting†assets, and they lose value every day. The buyer gets hurt from time decay and the seller benefits from it. And time decay is becoming more exponential. It is also the great equalizer between the profiles of a buyer and seller of Options. Time decay is the great equalizer in the risk / reward profiles of buyers and sellers of Options. Several intermediate and advanced strategies are based on selling the premium (option sellers) and these positions make a profit due to time decay in the value of these options over a period of time.What you will masterWhat is time decay and how does it benefit Option sellersA complete recap of buyer and sellerWhy does not the seller have the options?Why is the best option between buyers and sellers?Apply the concept of time to our real world examplesHow can we observe Time in Options in the financial marketsDemonstration of time decay using AAPL OptionsSECTION II – IMPLIED VOLATILITY AND OPTIONS PRICESImplied Volatility is the “wildcard†in Option prices. Ignore it, and you will pay a price. In fact, it’s so important we have at least four different varieties – Volatility, Implied Volatility, Historical Volatility, and Future or Expected Volatility. We use the real-world examples to explain the concept of Volatility in simple terms. Then we study how Volatility is quantified in Stocks and Options. And how Volatility finds a back-door. Implied Volatility considerations are critical when choosing between buyer and seller profile. NFLX and CAT options that we should make it clear that this is all about.What you will masterHow are Option prices?Why is it difficult to calculate or determine? Implied Volatility of an OptionWhy is it called “implied†VolatilityHow Does It Involve Volatility?Why is it the “wildcard†in Option pricesUnderstand a real world example of VolatilityWhat is the relationship between Option prices and Implied VolatilityHow should I buy and sell at Implied Volatility?Are some strategies better for high volatility situationsHow We Can Observe Implied Volatility In Real Option PricesSECTION III – GREEKS, DELTA, GAMMA, VEGA, THETA OPTIONIf you’re the pilot of an aircraft, the Greeks are your instrument panel. If you do not manage your instrument panel properly, well … you get the picture. Understanding the Greeks are absolutely critical to every option position. Greeks – Delta, the king of all Greeks. Gamma – the silent operator. Theta – every Option seller’s dream. And Vega – Watch out for this one .. Options tend to ignore the Greeks. Master the Greeks and you’ll shave off months of learning curve. Not to mention, you can fly your aircraft on “auto-pilot†(with help from the Greeks).What you will masterThe oven Greeks that governHow to have individual impactsWhy is the king of all GreeksWhat do we mean by directional riskHow does each Greek affect a buyer and a seller of Options?Why the Greeks are critical to understanding your Option positionHow the Greeks impact the choice of “moneyness†and expiry seriesSECTION IV – MARKET OPTIONS STRUCTURE, TERMINOLOGY, MARKET MAKERS AND MOREThe Options market has a number of terms that we need to be aware of. Starting with terminology differences like “Long†and “Shortâ€, we look at all the details that go into the Options market. We explain the important processes like Exercise and Assignment, Expiry series, Bid-Ask spreads, Brokerage and transaction costs and various other details. What is Open Interest and Why is it important, and what is the role of a Market Maker. We study the different types and make them more important for the average investor. We also discuss Regulation Margin as it applies to Options as well as Portfolio margin.What you will masterWhat does Open Interest tell us aboutWhat is Exercise and AssignmentWhat can Open Interest tell us about general feeling about the stockWhat are the different types and which ones are the bestWhat is the role of Market Makers on the Exchange Options?Marginalized margin and what is margin margin
 Harmonic Patterns for ThinkorSwim Bat, Butterfly, Crab, and Gartley
Harmonic Patterns for ThinkorSwim Bat, Butterfly, Crab, and Gartley
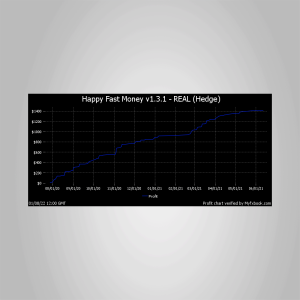 Happy Fast Money EA v1.3
₹14,774.00
Happy Fast Money EA v1.3
₹14,774.00






